Resource
- What Is a Laminar Flow Hood?
- Key Features:
- Types of Laminar Flow Hoods:
- What Is a Fume Hood?
- Key Features:
- Types of Fume Hoods:
- Key Differences Between Laminar Flow Hoods and Fume Hoods
- Which One Do You Need?
- Choose a fume hood if you work with volatile chemicals, acids, or toxic substances.
- Energy Consumption: Laminar Flow Hoods vs. Fume Hoods
- Laminar Flow Hoods: Energy-Efficient Contamination Control
- Fume Hoods: Higher Energy Demand for Safety
- Key Takeaways for Lab Managers
- Cost Considerations
Laminar Flow Hood vs. Fume Hood: Choosing the Right Lab Equipment for Your Needs
When setting up a laboratory, selecting the right equipment is crucial for safety, efficiency, and workflow optimization. Laminar Flow Hoods and Fume Hoods are two common pieces of lab equipment, each serving distinct functions and applications. This article explores the key differences between these two devices, helping you choose the most suitable one based on your laboratory's needs. Laminar flow hoods are primarily used to protect samples from contamination, making them ideal for tasks requiring sterile conditions. On the other hand, fume hoods are designed to protect users from hazardous gases, vapors, and chemicals. Understanding their operating principles, suitable applications, and energy efficiency differences will help you select the best equipment for your lab, ensuring safety and research effectiveness.
When setting up a laboratory, selecting the right containment equipment is critical for safety, efficiency, and workflow optimization. Two essential pieces of equipment—laminar flow hoods and fume hoods—serve distinct purposes in different lab environments. Understanding their differences will help you make the best choice for your research or industrial applications.
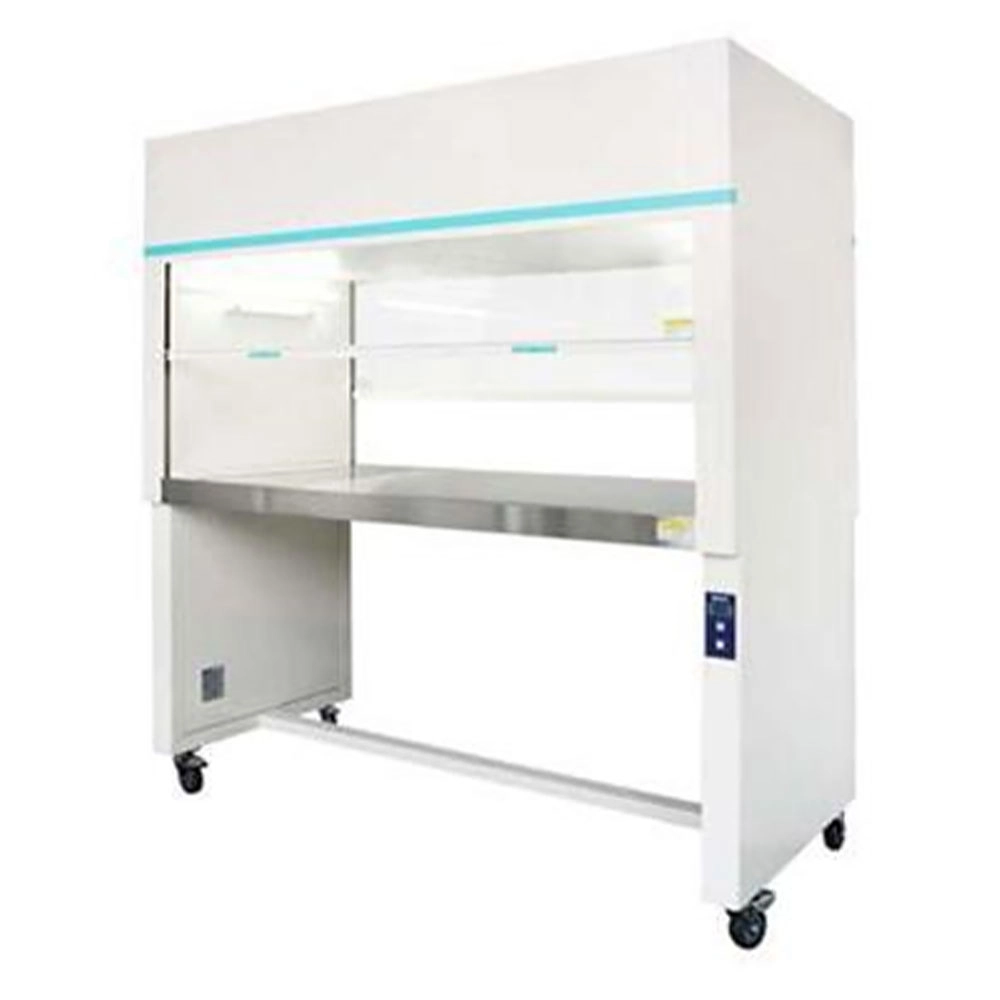
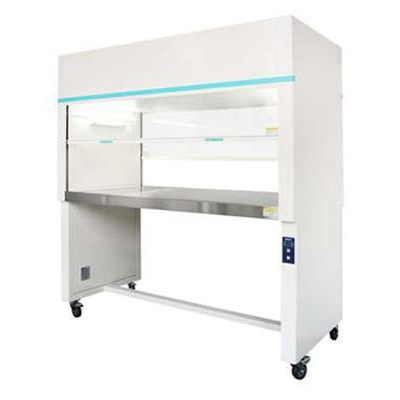
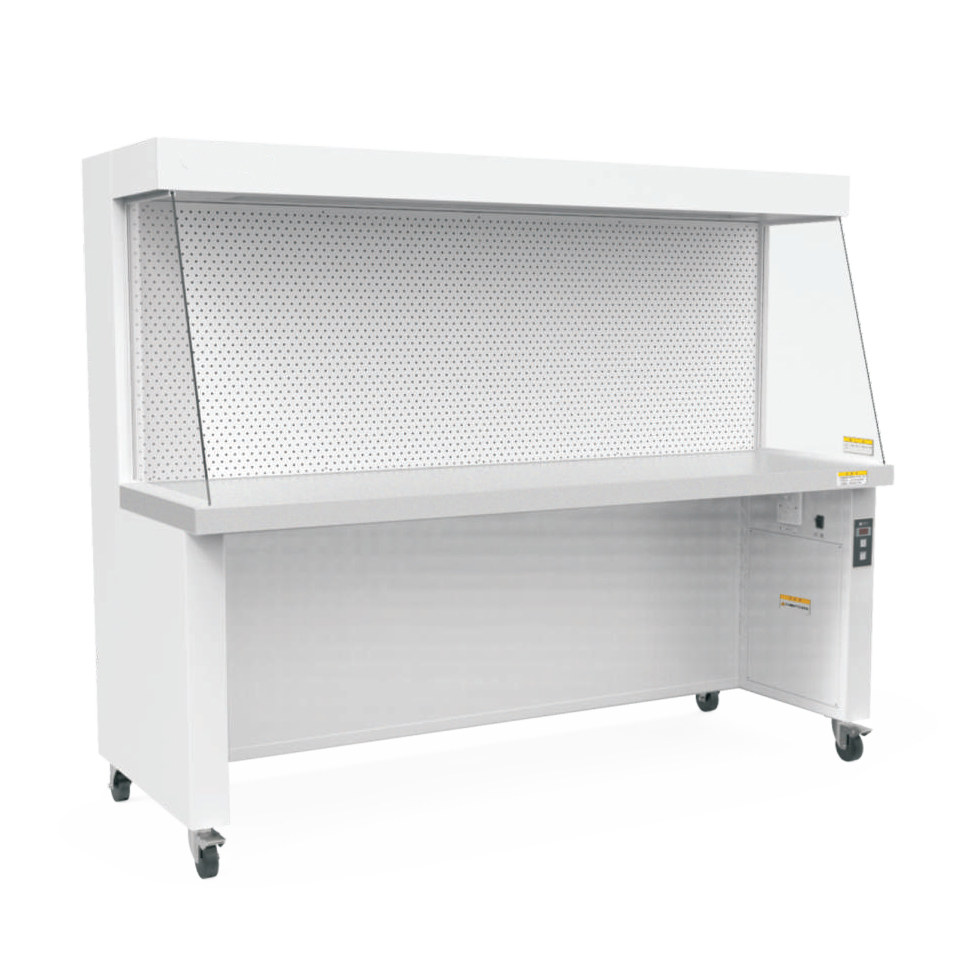
What Is a Laminar Flow Hood?
A laminar flow hood (also known as a clean bench) provides a sterile, particle-free workspace by directing HEPA-filtered air in a unidirectional flow. These hoods are commonly used in microbiology, pharmaceutical research, and electronics manufacturing where contamination control is crucial.The primary goal is product protection rather than user protection.
Key Features:
HEPA-filtered airflow (either vertical or horizontal)
Protects samples from contamination (not the user)
Ideal for sensitive processes like tissue culture, media preparation, and sterile packaging
Types of Laminar Flow Hoods:
Horizontal Flow: Air moves directly toward the user (best for non-hazardous materials).
Vertical Flow: Air descends from the top, reducing turbulence (common in medical and pharmaceutical labs).
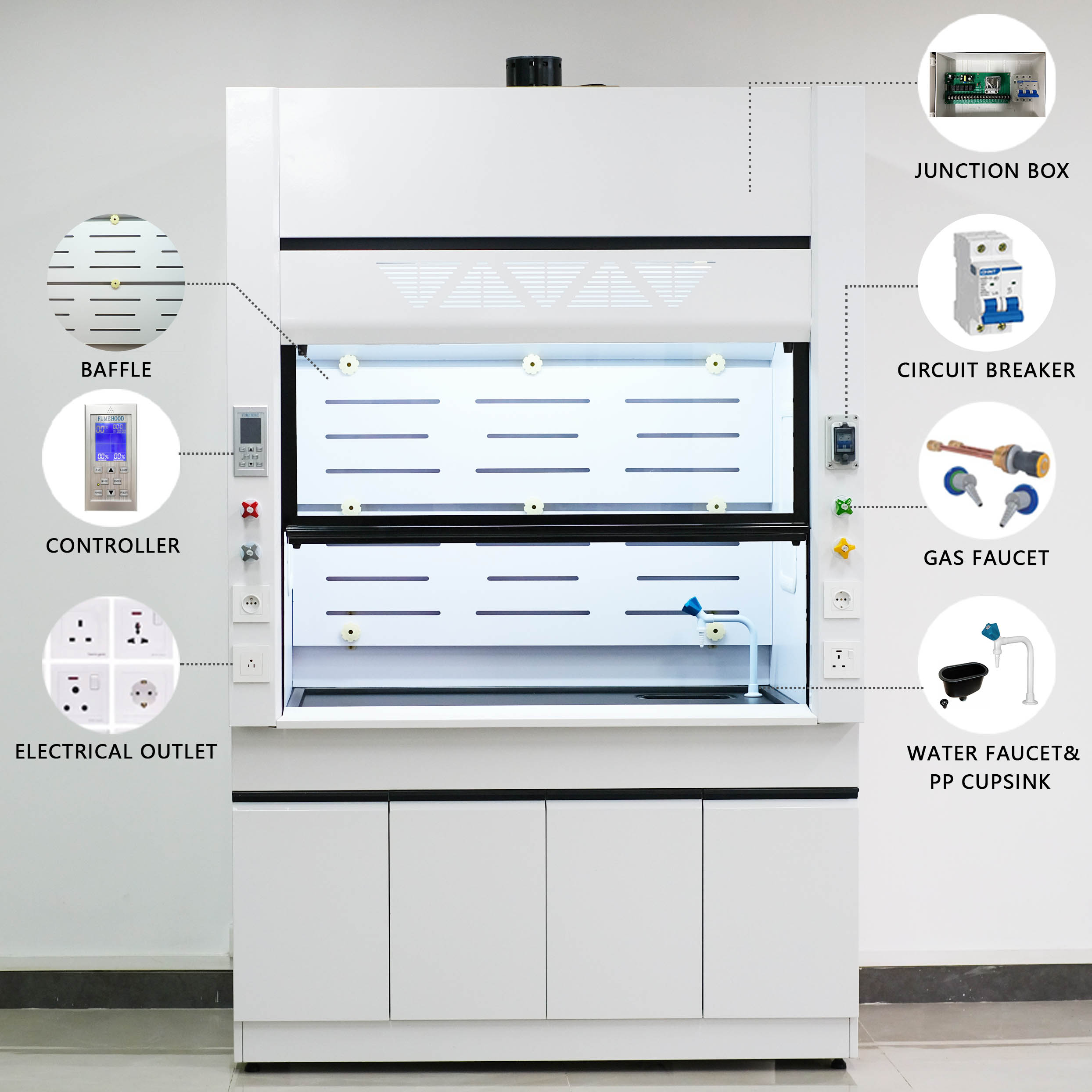
What Is a Fume Hood?
A fume hood is designed to protect the user from exposure to hazardous chemicals, vapors, and fumes. It works by drawing air inward and venting it outside or through filtration systems. The airflow moves away from the user, carrying potentially dangerous substances out of the breathing zone.
Key Features:
Chemical-resistant construction (often with epoxy or stainless steel)
Airflow containment to prevent exposure to toxic substances
Essential for chemical handling, solvent use, and toxic experiments
Types of Fume Hoods:
Fume Hoods: Vents contaminants outside the lab.
Ductless (Recirculating) Fume Hoods: Uses carbon filters to clean and recirculate air.
Perchloric Acid Hoods: Specialized for corrosive acid handling.
Key Differences Between Laminar Flow Hoods and Fume Hoods
|
Feature |
Laminar Flow Hood |
Fume Hood |
|
Primary Purpose |
Protects samples from contamination |
Protects the user from hazardous fumes |
|
Airflow Direction |
Unidirectional (HEPA-filtered)、 Either horizontally (across the work surface toward the user) or vertically (from top to bottom |
Inward 、upward(captures and vents fumes) |
|
Best For |
Sterile work, cell culture, electronics |
Chemical handling, toxic substances |
|
User Protection? |
No |
Yes |
|
Common Industries |
Pharma, biotech, medical labs |
Chemistry, industrial labs, research |
Which One Do You Need?
Choose a laminar flow hood if you need a contamination-free zone for sensitive materials.
Ex:
Pharmaceutical compounding
Cell culture work
Sterile medical device assembly
Microbiological research requiring aseptic conditions
Electronics manufacturing
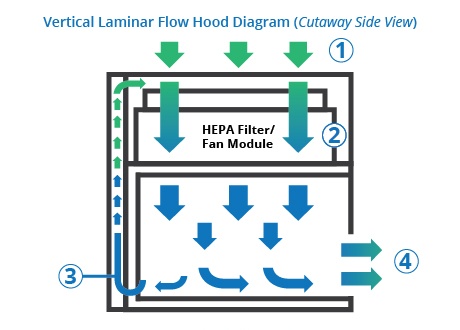
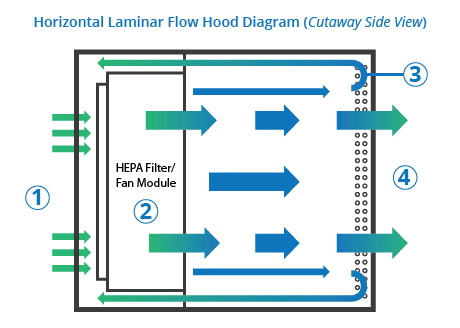
The physical construction of these systems reflects their different purposes. Laminar flow hood typically feature transparent sides or an open front, with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) or ultra-low particulate air (ULPA) filters positioned to create the characteristic laminar airflow pattern.
Choose a fume hood if you work with volatile chemicals, acids, or toxic substances.
Ex:
Chemical reactions involving volatile compounds
Procedures generating hazardous vapors or fumes
Handling of toxic substances
Work with strong acids, bases, or solvents
Experiments producing noxious odors
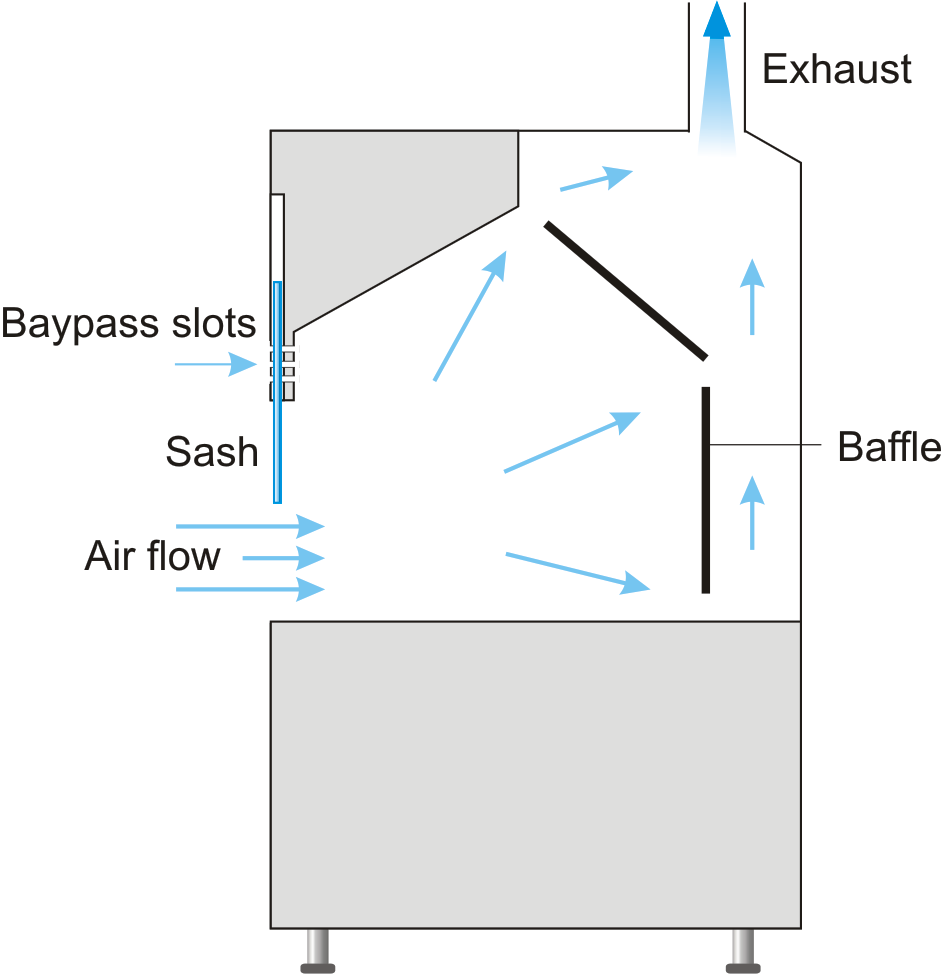
Fume hood have a more enclosed design with a movable sash that can be adjusted to optimize airflow and provide a physical barrier between the user and the workspace. They connect to exhaust systems that filter and/or direct air outside the building.
In some cases, labs may require both—using a fume hood for chemical prep and a laminar flow hood for sterile procedures.
Energy Consumption: Laminar Flow Hoods vs. Fume Hoods
Energy efficiency is a crucial factor when selecting lab ventilation equipment. Laminar flow hoods and fume hoods differ significantly in their power requirements, impacting both operational costs and environmental sustainability.
Laminar Flow Hoods: Energy-Efficient Contamination Control
Laminar flow hoods recirculate HEPA-filtered air within the workspace, requiring energy primarily for:
Blower motor operation (to maintain unidirectional airflow)
Filter maintenance (periodic HEPA filter replacements)
Since they do not exhaust air externally, laminar flow hoods have lower energy demands and place minimal strain on HVAC systems. This makes them a cost-effective choice for cleanroom applications, sterile processing, and other contamination-sensitive tasks.
Fume Hoods: Higher Energy Demand for Safety
Fume hoods prioritize user protection by continuously extracting hazardous fumes, which leads to greater energy consumption due to:
Constant air exhaust (requiring powerful blowers)
HVAC compensation (labs must replace conditioned air, increasing heating/cooling costs)
Additional ventilation needs (ductwork, makeup air systems)
The energy impact varies based on:
Ducted vs. ductless designs (ducted hoods typically use more energy)
Face velocity settings (higher airflow = greater energy use)
Lab climate control requirements (temperature/humidity stability)
Key Takeaways for Lab Managers
Laminar flow hoods = Lower energy costs, ideal for contamination control.
Fume hoods = Higher energy use but essential for chemical safety.
Hybrid solutions (e.g., variable-air-volume fume hoods) can optimize efficiency.
Cost Considerations
The initial purchase cost for laminar flow hood is generally lower than for fume hood. However, the total cost of ownership includes installation, maintenance, and operational expenses.
Fume hood typically have higher installation costs due to the need for ductwork, exhaust systems, and potentially makeup air systems. Their ongoing operational costs are also higher because of greater energy consumption.
Tip: Laminar flow cabinets cannot replace fume hoods.
These systems serve fundamentally different purposes. Laminar flow hoods protect materials from contamination but offer no protection against hazardous fumes. Using a laminar flow hood for chemical work that generates vapors could expose the user to dangerous substances.
MAX LAB Solutions
At MAX LAB, we provide high-quality laminar flow hoods and fume hoods tailored to your lab’s needs. Our equipment is built for precision, safety, and durability—ensuring optimal performance for your research.
Need help deciding? Contact our experts today for a consultation!

Why We Choose to Be Your Lab Furniture Solution Provider, Not Just a Manufacturer

Max Lab Introduction

Electronics Lab Bench vs Chemistry Lab Bench: What You Need to Know

What Is an Air Shower for Cleanroom?
For Company
What types of companies do you work with?
We have worked with a wide range of companies, from small startups to large, multinational corporations. Our expertise in the laboratory furniture industry enables us to meet the needs of various sectors, including healthcare, research, education, pharmaceuticals, and industrial labs.
For After-Sales Support
Why choose your company?
We have been engaged in the manufacturing of various packing machines professionally over 15 years, and we can provide better after-sales service.
For Products
Do you offer ergonomic solutions for lab furniture?
Yes, our laboratory furniture includes ergonomic designs such as height-adjustable lab benches and chairs that reduce strain during long hours of work.
FAQS
How can I request a quote?
Simply contact us or fill out our online form with your project details. Our team will respond promptly with a free quote.
For Customization
Can I customize the size and configuration of my lab furniture?
Yes, we offer full customization for laboratory benches, modular systems, and storage units to meet your specific space and functional needs.

Get in touch with us
If you have any comments or good suggestions, please leave us a message; later our professional staff will contact you as soon as possible.








 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
MaxLabFurniture
MaxLab Furniture
daihongada
Max Laboratory