Lab Sink Cabinet Buying Guide: Materials, Sizes, and Features
- Materials: Comparing Lab Sink Options for Durability and Chemical Resistance
- Stainless Steel: Strength and Heat Resistance
- Epoxy Resin: Chemical Resistance for Analytical and Teaching Labs
- Polypropylene, Ceramic and Other Options
- Sizes, Configurations and Installation Types
- C-type, Floor-mounted and H-type Structures
- Standard Sink Sizes and Bench Integration
- Plumbing, Drainage and Waste Handling
- Features, Accessories and Safety Considerations
- Faucets, Drains and Overflow Options
- Chemical-resistant Coatings, Liners and Work Surfaces
- Ergonomics, Storage and Temporary Holding
- Maintenance, Compliance and Choosing a Supplier
- Cleaning, Decontamination and Maintenance Best Practices
- Standards, Regulations and Documentation
- Why Supplier Selection Matters: Reliability, Warranties and Support
- Brand Advantages — Why Choose Our Lab Sink Cabinet
- FAQ — Common Questions About Lab Sink Cabinets
- Q: Which sink material is best for strong acids?
- Q: Can I retrofit a lab sink cabinet into an existing bench?
- Q: How do I handle corrosive waste from a lab sink?
- Q: What maintenance is required for epoxy resin sinks?
- Q: Are hands-free faucets recommended for lab sinks?
- Q: What documentation should suppliers provide?
Choosing the right lab sink cabinet is crucial for safety, durability and workflow efficiency in chemistry labs, teaching labs, biopharmaceutical facilities and testing departments. This guide explains how material choice, cabinet size and structural type affect chemical resistance, heat tolerance, maintenance and installation, and provides practical recommendations for selecting a lab sink that integrates with full laboratory bench systems while meeting drainage, cleaning and storage needs.
Materials: Comparing Lab Sink Options for Durability and Chemical Resistance
Stainless Steel: Strength and Heat Resistance
Stainless steel sinks (typically 304 or 316 grades) are widely used where heat resistance, impact resistance and ease of cleaning are priorities. 316 stainless offers better corrosion resistance to chlorides and is often recommended where aggressive solvents or saline solutions are used. Stainless sinks integrate well into steel or modular bench frames and are compatible with many lab faucets and drains.
Epoxy Resin: Chemical Resistance for Analytical and Teaching Labs
Epoxy resin sinks and countertops are formulated for excellent resistance to a broad spectrum of acids, bases and solvents. They are non-porous and provide a smooth surface that tolerates many reagents used in chemistry labs and teaching environments. Epoxy resin is often used for lab benches and integrated sink basins because it can be molded to seamless shapes, minimizing crevices where contaminants can accumulate.
Polypropylene, Ceramic and Other Options
Polypropylene (PP) sinks are highly chemical-resistant to many strong acids and bases, making them suitable for corrosive waste handling; they are also lightweight and inexpensive. Ceramic sinks are highly resistant to many acids and offer scratch resistance but can chip under impact or thermal shock. Selection should consider the most common chemicals and temperatures the sink will encounter to ensure long-term durability.
Below is a concise comparison table summarizing typical properties of common lab sink materials:
| Material | Chemical Resistance | Heat Resistance | Durability / Impact | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | Good; 316 better vs chlorides | High | High (dent susceptible) | General labs, wash stations, autoclave areas |
| Epoxy Resin | Very good vs many acids/bases/solvents | Moderate | Good (surface scratches can occur) | Analytical benches, teaching labs |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Excellent vs strong acids & bases | Low-moderate | Moderate (can deform at high temps) | Corrosive waste sinks, chemical handling |
| Ceramic | Good vs acids | High | Moderate (brittle) | Teaching labs, wash sinks |
When selecting a lab sink, consult chemical compatibility charts for specific reagents. Authoritative resources such as the CDC laboratory biosafety guidance provide broader context on lab design and materials used in safe laboratory environments (CDC - Laboratory Biosafety), and general laboratory equipment information can be found in industry references like Wikipedia's laboratory equipment overview (Laboratory equipment — Wikipedia).
Sizes, Configurations and Installation Types
C-type, Floor-mounted and H-type Structures
The Lab Sink Cabinet is designed to support multiple structural configurations, offering C-type, floor-mounted and H-type options to match lab layouts and load requirements. C-type (open-back) cabinets allow for easy plumbing access and legroom for seated work; floor-mounted cabinets give maximum storage and stability; H-type (double-sided) configurations are ideal for island benches where sinks and faucets are needed on both sides.
Each structural type influences workflow and plumbing routing. For example, floor-mounted cabinets can conceal drains and waste traps behind doors, improving aesthetics and creating secure storage for chemical-compatible drums, while C-type cabinets are easier to retrofit into existing bench runs.
Standard Sink Sizes and Bench Integration
Lab sink basins come in a range of sizes: small single bowls (~300 x 300 mm) for hand wash and small rinsing tasks, medium basins (~400 x 500 mm) for general cleaning, and deep trough options for multiple users or large glassware. When integrating with a laboratory bench system, consider the work surface height (typically 900–950 mm for standing benches, 740–760 mm for seated lab furniture), sink cutout dimensions, and edge treatment to maintain a seamless junction between the sink and bench top.
Plumbing, Drainage and Waste Handling
Proper drainage is essential. Lab sinks should be plumbed with appropriately sized traps and corrosion-resistant piping. Consider separate drains or dedicated waste lines for chemical sink waste vs. general sink waste. Where required by safety protocols, install acid-resistant drain lines and secondary containment beneath the sink. Consult local plumbing codes and lab safety regulations from authorities like OSHA for laboratory-specific guidance (OSHA - Laboratory Safety).
Features, Accessories and Safety Considerations
Faucets, Drains and Overflow Options
Lab faucets should be chemical-resistant and may include gooseneck, thermostatic mixing, or hands-free (sensor) options. Drain fittings, basket strainers and quick-release traps reduce clogging and simplify maintenance. Overflow protection is important for sinks used with large volumes — integrated overflows or anti-siphon devices help avoid accidental spills into cabinetry.
Chemical-resistant Coatings, Liners and Work Surfaces
Where full material replacement is not feasible, chemical-resistant liners or coatings for cabinets and sink surrounds extend service life. Epoxy coatings, phenolic resin liners and specialized polymer trays can protect underlying metal structures from corrosive vapors and spills. For bench integration, choose worktops (epoxy, phenolic, stainless steel) that are compatible with the sink material to avoid galvanic corrosion or differential wear.
Ergonomics, Storage and Temporary Holding
Good sink cabinet design balances ergonomics and storage. Cabinets with adjustable shelves, sealed drawers and removable trays allow temporary storage of glassware and minimize contamination risk. Consider the placement of hazardous-waste containers, eyewash stations, and fume hoods relative to the sink for safe workflow. Height-adjustable benches and sink lip designs reduce repetitive strain during long procedures.
Maintenance, Compliance and Choosing a Supplier
Cleaning, Decontamination and Maintenance Best Practices
Regular cleaning and preventive maintenance extend the life of lab sinks and cabinets. For stainless steel, use non-chloride cleaners and avoid abrasive pads that scratch and weaken protective films. For epoxy and polymer sinks, consult manufacturer instructions for solvent-compatible cleaners. Implement a maintenance schedule that includes drain flushing, trap inspection and seal checks to prevent leaks and contamination.
Standards, Regulations and Documentation
Ensure the sink cabinet and installation comply with applicable standards for laboratory safety, plumbing and chemical handling. Relevant references include OSHA lab safety guidance (https://www.osha.gov/laboratory), CDC biosafety resources (https://www.cdc.gov/labs/index.) and product-specific data sheets. Suppliers should provide material safety documentation, chemical compatibility tables and installation manuals to support compliance and risk assessments.
Why Supplier Selection Matters: Reliability, Warranties and Support
Choose a supplier with proven experience in lab furniture and plumbing integration. Look for product warranties, on-site support, and the ability to customize sink basins, cabinet finishes and plumbing fittings. A reputable manufacturer will provide technical drawings, CAD files and clear lead times to coordinate installation with other bench systems.
Brand Advantages — Why Choose Our Lab Sink Cabinet
The Lab Sink Cabinet is designed for chemistry labs, teaching labs, biopharmaceutical facilities and testing departments, and can be seamlessly integrated into complete laboratory bench systems. The product offers C-type, floor-mounted and H-type structures, combined with a chemical-resistant lab sink and lab faucet to meet cleaning, rinsing, drainage and temporary storage needs.
Key brand advantages:
- Modular integration: Designed to fit standard lab bench systems with easy plumbing access for retrofit or new installations.
- Material choice and customization: Multiple sink materials and cabinet finishes available to match your chemical handling needs and budget.
- Safety-first design: Optional secondary containment, sealed storage and compatibility with dedicated waste lines.
- Technical support: CAD drawings, installation guidance and post-sale service to ensure smooth commissioning.
Our product documentation includes chemical compatibility tables and maintenance guides. When comparing suppliers, verify third-party references and case studies demonstrating long-term performance in environments similar to yours.
FAQ — Common Questions About Lab Sink Cabinets
Q: Which sink material is best for strong acids?
A: Polypropylene or high-grade epoxy resin are typically best for strong acids, but the exact choice depends on concentration and temperature. For chloride-containing acids at elevated temperatures, consult chemical compatibility charts; 316 stainless may be required for some mixtures.
Q: Can I retrofit a lab sink cabinet into an existing bench?
A: Yes. C-type (open-back) and floor-mounted cabinets are commonly used for retrofits. Ensure plumbing routing and bench cutouts align; request supplier CAD files and measure bench heights and cutout sizes before ordering.
Q: How do I handle corrosive waste from a lab sink?
A: Segregate corrosive waste into appropriate containers and use dedicated acid-resistant drain lines where permitted. Follow local environmental and safety regulations for disposal. Use labeled, corrosion-resistant storage within the cabinet if temporary holding is needed.
Q: What maintenance is required for epoxy resin sinks?
A: Clean with mild detergents or manufacturer-recommended cleaners; avoid aggressive solvents that may affect the resin. Inspect for surface crazing or chemical staining and repair per supplier guidelines. Rinse drains regularly to avoid buildup.
Q: Are hands-free faucets recommended for lab sinks?
A: Hands-free (sensor) faucets reduce cross-contamination and are beneficial in many lab settings, particularly teaching labs and high-traffic wash stations. Consider compatibility with water supply pressure and the need for battery or hard-wired power.
Q: What documentation should suppliers provide?
A: Request material safety data sheets (MSDS) for the sink materials, installation manuals, chemical compatibility charts, CAD drawings and warranty terms. Documentation helps with procurement approvals and compliance checks.
After narrowing down cabinet configurations, many labs prioritize safety and durability, making chemical-resistant lab sink solutions for safety and durability a critical consideration.If you have specific requirements (chemical lists, bench dimensions, or plumbing constraints), our technical team can provide tailored recommendations and CAD layouts to ensure the Lab Sink Cabinet fits your lab workflow and safety protocols.
Contact us to view the Lab Sink Cabinet or request a quote: reach our customer service at sales@example.com or click to view product details and downloadable drawings. For immediate assistance, call our support line during business hours.
What are the different types of Laboratory?
Ergonomic Principles in Lab Furniture Design
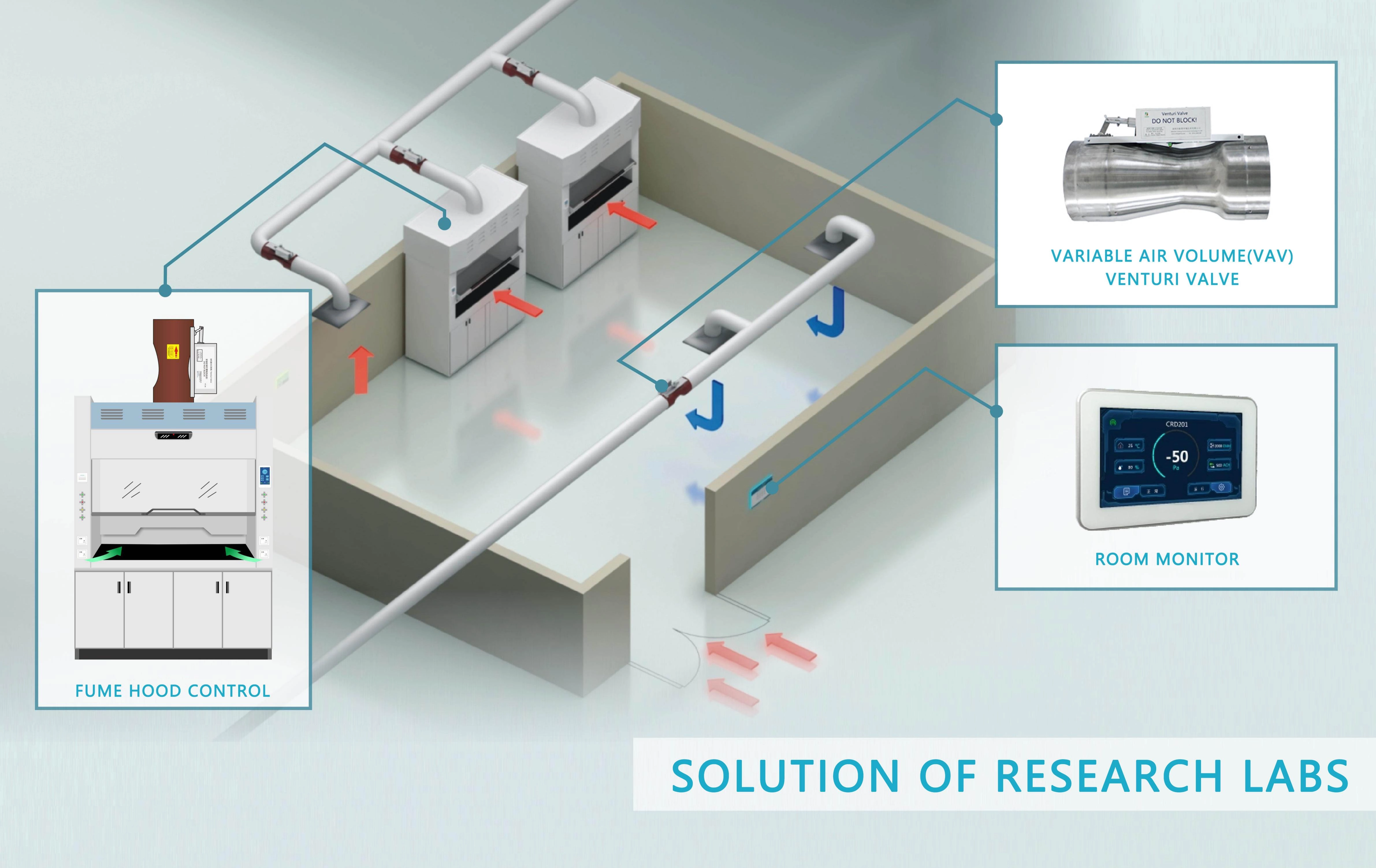
Retrofit Strategies for Installing Variable Air Volume Fume Hoods

Maintenance Protocols That Extend Lab Countertop Lifespan
For Customization
Can you create a lab design layout for us?
Yes, we'll provide preliminary layout, confirm 3D drawings and rendering drawings.
For Company
How do I get in touch with your sales team?
You can reach our sales team via email at ada@maxlabfurniture.com, by phone at +86 132 4232 3168, WhatsApp:+86 132 4232 3168, or through the contact form on our Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/MaxLabFurniture
For Logistics
Do you offer express shipping options?
Yes, we offer express shipping for urgent orders. Please contact our sales team to inquire about availability and additional costs.
FAQS
Do you offer custom design services?
Yes, we provide full design support tailored to your lab’s specific needs, including layout planning and furniture customization.
For Products
Can I change the size and color?
Yes, of course. Custom-made items are welcome, if you have any need, please feel free to contact us at anytime.

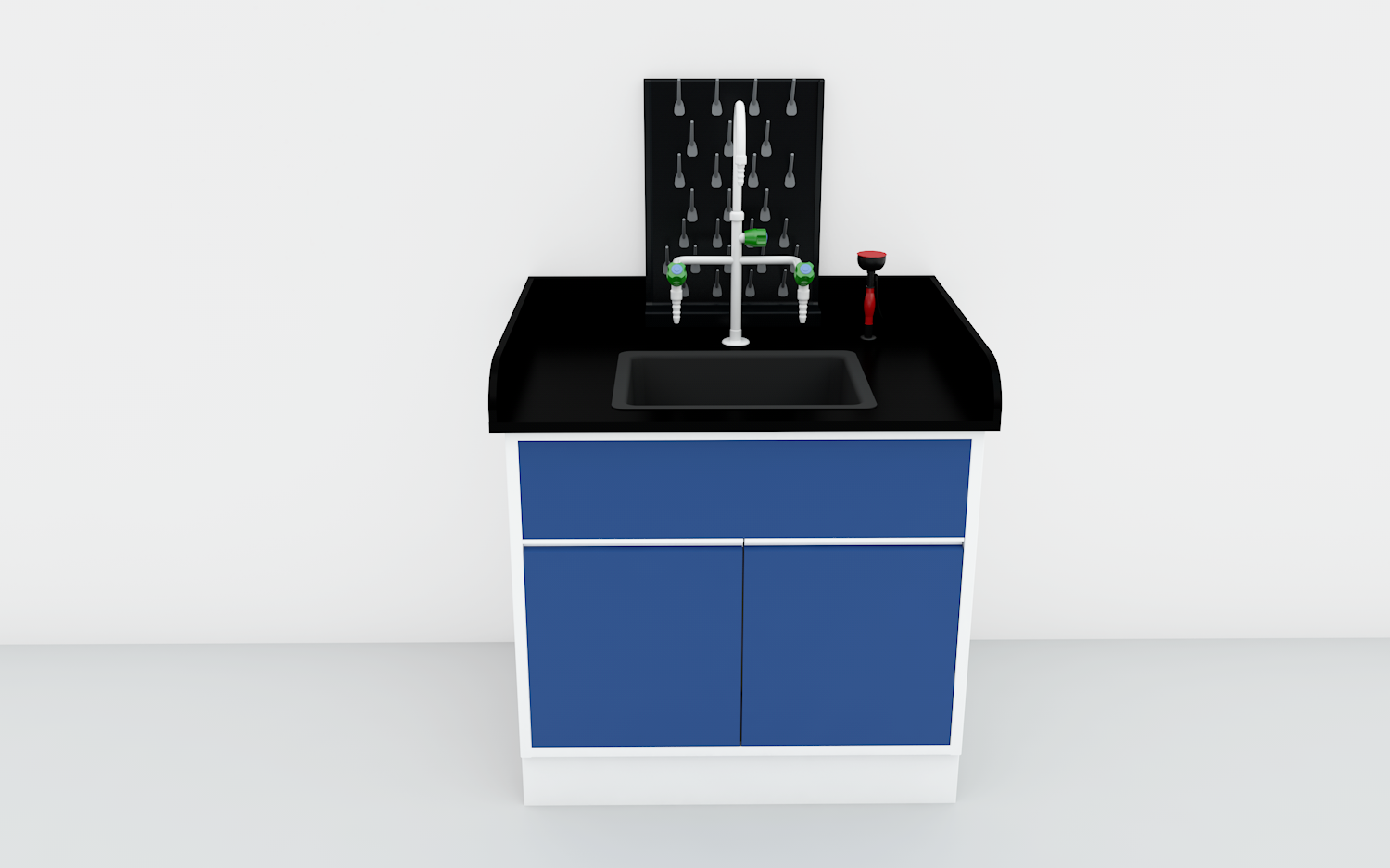
Lab Sink LS-08
The LS-08 Round Cup / Funnel Sink is a small-diameter, deep cup sink designed as a funnel-type drain point on laboratory worktops. Constructed from chemical-resistant black PP, it features an extended threaded outlet that connects directly to drain piping.
This design is perfect for apparatus drain lines, RO reject water, condensate and other continuous or intermittent discharges where an open, funnel-like inlet is required.

Floor Mounted Lab Bench
Our Floor Mounted Lab Bench is an essential, high-efficiency workspace for laboratories, made from high-quality steel-wood or corrosion-resistant stainless steel materials to ensure exceptional durability and stability. The unique floor-mounted design effectively reduces vibration, optimizes space usage, and provides a safe and tidy laboratory environment.
Customizable storage solutions help organize lab equipment efficiently, while the easy-to-clean surface maintains laboratory hygiene. It is widely suitable for research institutions, educational laboratories, and the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.

Fume Hood
The fume hood provides safe ventilation to protect against exposure to hazardous or toxic fumes, vapors, or airborne particulate. It is primarily used in laboratory and manufacturing applications to protect the user or environment outside the hood, but can also be used to protect the materials or experiment under the hood.
APPLICATION
Chemistry Lab, physics Lab, biological analysis, pharmaceutical medicine analysis, biological pharmaceutical, plant culture, environmental testing and electronic instrumentation scientific research and so on.

Flammable Storage Cabinet
Safety Cabinets store flammable liquids, corrosives, pesticides and other hazardous materials. All fire-resistant safety cabinets by meet fire codes and regulations for safety storage.
To help protect your people and facility from a potential fire, safety cabinets are engineered to safely contain flammable fuels, solvents, and chemicals. Safety cabinets can not only help everyone store chemicals reasonably, save chemical supplies, but also save human resources, and avoid fires caused by chemicals with the greatest strength.


 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
MaxLabFurniture
MaxLab Furniture
daihongada
Max Laboratory