How to Choose the Right Lab Sink for Your Facility
- Understanding functional requirements for your lab sink
- Assess the laboratory activities and chemical compatibility
- Determine sizing, flow rates and drainage needs
- Plan for ergonomics and user safety
- Design and configuration options for Lab Sink Cabinets
- Lab Sink Cabinet structures: C-type, floor-mounted and H-type
- Integrated faucet and accessory choices
- Storage, containment and secondary spill management
- Materials, durability and maintenance
- Comparing common sink materials
- Choosing cabinet construction and finishes
- Cleaning, decontamination and lifecycle maintenance
- Installation, compliance and lifecycle costs
- Plumbing integration and waste segregation
- Regulatory standards and safety guidance
- Budgeting, total cost of ownership and ROI
- Selecting the right sink solution: practical decision checklist
- Quick checklist for specification and procurement
- Working with manufacturers and installers
- Case example: Chemistry teaching lab retrofit
- Brand advantage and why our Lab Sink Cabinet stands out
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What sink material is best for a general chemistry lab?
- Q: Can a lab sink drain go directly to the sanitary sewer?
- Q: Are sensor faucets suitable for labs?
- Q: How often should lab sink drains and traps be inspected?
- Q: What warranty and documentation should I request?
Choosing the right lab sink is more than picking a basin — it affects chemical safety, waste handling, ergonomics, and long-term operating costs. This article walks through practical evaluation criteria, configuration choices, materials comparisons, installation and compliance considerations, and maintenance best practices. It also explains how the Lab Sink Cabinet (available in C-type, floor-mounted and H-type configurations) integrates with lab benches and plumbing systems to deliver a durable, chemical-resistant solution for teaching labs, chemistry labs, biopharma facilities and testing departments.
Once you understand how to choose the right lab sink for your facility, the next step is evaluating cabinet structure, dimensions, and accessories through a detailed lab sink cabinet buying guide: materials, sizes, and features.
Understanding functional requirements for your lab sink
Assess the laboratory activities and chemical compatibility
Begin by mapping the primary activities performed at each sink station. Sinks used for general glassware cleaning will have different needs than sinks for chemical neutralization or biological sample rinsing. Identify the most corrosive chemicals, solvents and temperatures the sink will encounter. Documenting typical usage helps select appropriate sink materials (e.g., epoxy resin, stainless steel, polypropylene) and compatible lab faucet finishes and seals. For broad guidance about laboratory equipment types and uses, see the overview on Laboratory equipment.
Determine sizing, flow rates and drainage needs
Size affects both usability and code compliance. Consider bowl dimensions and depths for comfortable access and adequate splash containment. Specify flow rates and choose faucets with flow-control or aerators suited to tasks (low-flow for routine washing, higher flow for emergency rinsing). Drainage must tie into proper waste segregation (chemical vs. sanitary) and may require neutralization traps or waste sampling points. Engage plumbing early to confirm slope, trap locations and venting per local plumbing codes.
Plan for ergonomics and user safety
Place sinks at heights that minimize repetitive strain — adjustable or seated heights are often used in teaching labs. Consider integration with emergency eyewash and shower systems for stations handling hazardous substances. Anti-slip flooring, splash guards, and adequate lighting all reduce incident risk. OSHA provides laboratory safety guidance which is useful when planning equipment placement: OSHA Laboratory Safety.
Design and configuration options for Lab Sink Cabinets
Lab Sink Cabinet structures: C-type, floor-mounted and H-type
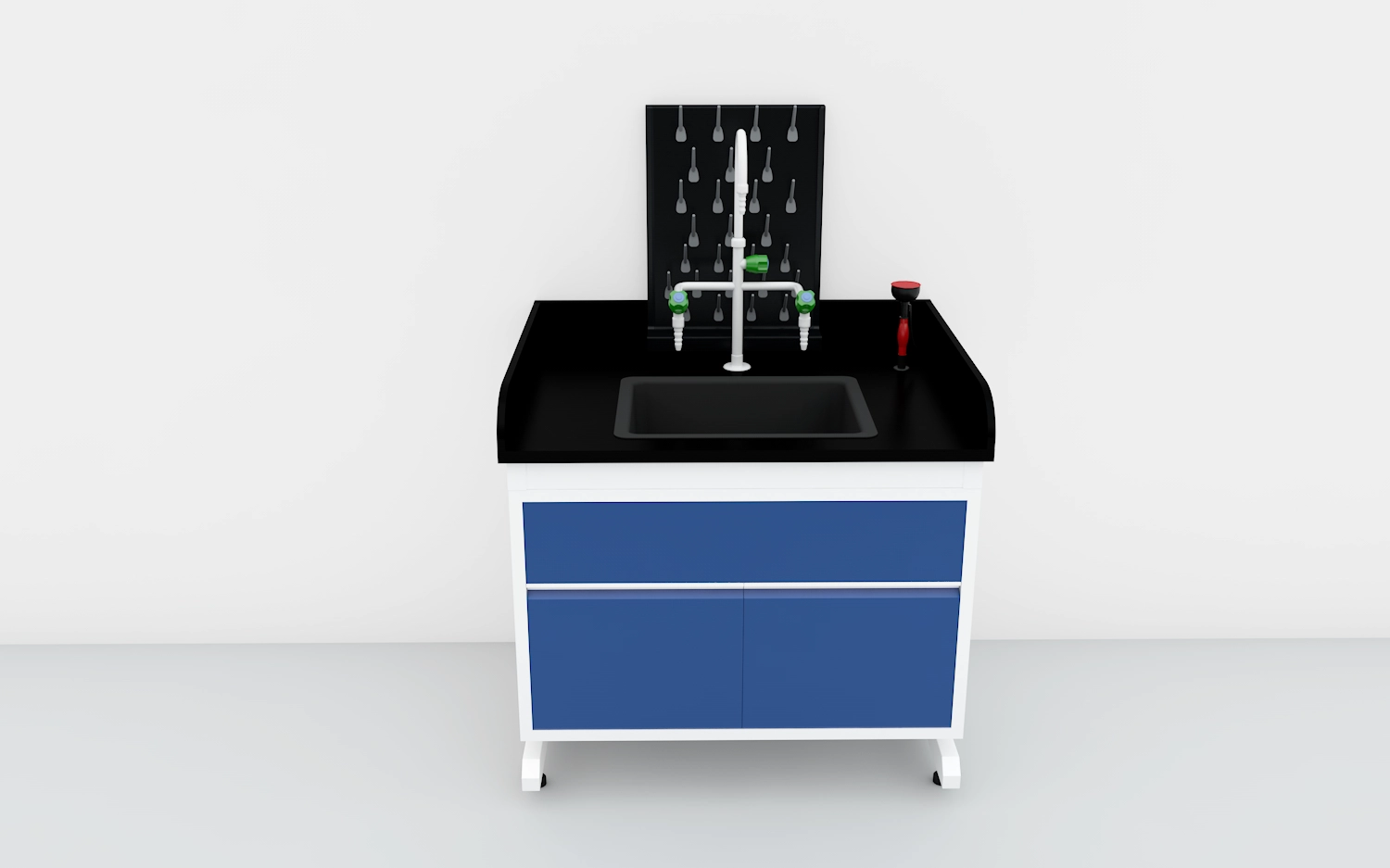
The Lab Sink Cabinet is designed for chemistry labs, teaching labs, biopharmaceutical facilities and testing departments, and can be seamlessly integrated into complete laboratory bench systems. The product offers C-type, floor-mounted and H-type structures, combined with a chemical-resistant lab sink and lab faucet to meet cleaning, rinsing, drainage and temporary storage needs.
C-type cabinets typically integrate under-counter storage with an inset sink, minimizing footprint while providing convenient access. Floor-mounted units are robust and ideal for heavy-use stations, while H-type configurations are designed for double-bench runs or islands where plumbing and access are required from both sides.
Integrated faucet and accessory choices
Choose between fixed or swing faucets, gooseneck vs. low-profile spouts, and consider hands-free (sensor) faucets to reduce contamination. For chemical handling stations, select faucets with PTFE or Viton seals and corrosion-resistant fixtures. Accessories such as pre-rinse sprayers, gooseneck rinsers, and sink baskets enhance function. Confirm compatibility of faucet threads and mounting holes with the cabinet and sink bowl design.
Storage, containment and secondary spill management
Lab Sink Cabinets can provide temporary storage for detergents and secondary containment for chemical bottles. For hazardous-liquid handling, integrate bunding or spill trays beneath sinks to capture leaks. Consider lockable compartments for corrosives and secure shelving that resists spilled chemicals. This reduces environmental exposure and simplifies cleanup procedures.
Materials, durability and maintenance
Comparing common sink materials
Selecting the right material is central to longevity and safety. Below is a comparison of common materials used for lab sinks and cabinets.
| Material | Chemical resistance | Durability & heat resistance | Maintenance | Best use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin | Excellent to strong for acids, bases; vulnerable to some solvents | High chemical & thermal resistance; can chip if impacted | Easy to clean; repairable surface | Chemistry labs, general-purpose sinks |
| Stainless steel (304/316) | Good to excellent; 316 better for chloride-rich environments | High impact & heat tolerance; may scratch | Sanitary and easy to sanitize; periodic polishing | Biopharma, wet labs needing sterilization |
| Polypropylene (PP) / Polyethylene (HDPE) | Very resistant to many acids/bases; better vs. solvents | Moderate; can deform under high heat | Simple cleaning; lighter weight | Corrosive chemical handling, specialty waste stations |
| Vitreous china / ceramic | Good to moderate; surface can be etched by strong acids | Brittle; high heat resistance but prone to chipping | Easy to clean but fragile | Teaching labs, low-corrosive environments |
Choosing cabinet construction and finishes
Cabinets should be constructed with chemical-resistant core materials and finishes (e.g., epoxy powder-coated steel, chemical laminate, or stainless steel faces). Shelving should support expected loads and resist corrosion. Consider toe-kick details for cleaning access and height adjustability for leveling on uneven floors.
Cleaning, decontamination and lifecycle maintenance
Define cleaning protocols based on sink usage—routine detergent washing, periodic neutralization for chemical residues, and sanitization cycles for biological work. Use compatible cleaners; avoid solvents that attack sink material. Maintain faucets, traps and seals with scheduled inspections to prevent leaks and clogging. Document maintenance to support compliance audits.
Installation, compliance and lifecycle costs
Plumbing integration and waste segregation
Coordinate early with plumbing and environmental health staff. Decide whether sink waste drains to sanitary sewer, chemical waste collection, or a neutralization system. Install proper traps and easy-access sampling ports if required. For labs handling hazardous wastes, ensure labeling and segregation align with local hazardous waste regulations.
Regulatory standards and safety guidance
Laboratory sinks and fixtures must be selected and installed with applicable safety and plumbing standards in mind. Refer to authoritative resources such as the NSF for sanitation performance and the CDC Laboratory Safety pages for biosafety practices. Local plumbing codes and building regulations will govern venting, backflow prevention and waste connections. General information on laboratory environments and safety is available from Wikipedia: Laboratory.
Budgeting, total cost of ownership and ROI
Calculate not only purchase cost but installation, downtime, maintenance, and replacement frequency. Higher upfront cost for a chemical-resistant epoxy sink with durable faucets may be justified by reduced replacement and repair costs in corrosive environments. Factor in staff time for cleaning and any required specialized maintenance. A lifecycle cost analysis clarifies trade-offs and supports procurement decisions.
Selecting the right sink solution: practical decision checklist
Quick checklist for specification and procurement
- Identify primary lab activities for the sink station (glassware wash, solvent use, biological rinsing, emergency eyewash).
- List the most aggressive chemicals and solvents used and required temperature range.
- Choose sink and cabinet material based on chemical compatibility and durability.
- Confirm plumbing route, waste segregation, and need for neutralization or sampling points.
- Decide on faucet type (sensor vs. manual), flow rate, and accessory needs.
- Plan for ergonomics, safety devices, and maintenance access.
- Obtain vendor documentation, chemical resistance charts and warranties.
Working with manufacturers and installers
Request product datasheets and chemical compatibility charts. Ask manufacturers for installation references and maintenance manuals. For complex facilities, request a site survey so the supplier can advise on cabinetry, plumbing interfaces, and integration with fume hoods or bench systems. Well-documented products and responsive technical support reduce integration risk.
Case example: Chemistry teaching lab retrofit
A mid-size university replaced outdated sinks with Lab Sink Cabinets in an H-type configuration for island benches. They selected epoxy-resin sinks and durable, single-lever faucets with low-flow aerators. The result: improved resistance to acids used in student labs, lower maintenance costs, and easier cleaning. The school coordinated with campus plumbing to upgrade neutralization and sampling points to remain compliant with waste handling rules.
Brand advantage and why our Lab Sink Cabinet stands out
Our Lab Sink Cabinet integrates proven cabinet architectures (C-type, floor-mounted and H-type) with chemical-resistant sinks and configurable lab faucets. Key advantages include:
- Modular design to integrate with most laboratory bench systems, reducing retrofit time.
- Multiple material options (epoxy, stainless steel, polypropylene) to match chemical compatibility needs.
- Industry-grade fittings and seals designed for durability in high-use environments.
- Accessible plumbing panels and removable trays to simplify maintenance and compliance inspections.
- Local technical support and documentation for installation, cleaning and safety protocols to meet EHS and institutional requirements.
When evaluating suppliers, request independent test results, user references and installation guidance to verify performance claims. Our product literature includes chemical resistance data, installation drawings and maintenance schedules to streamline procurement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What sink material is best for a general chemistry lab?
A: For most chemistry labs, epoxy resin sinks provide a balanced combination of chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness. For environments with significant chloride exposure or where sterilization is frequent, 316 stainless steel may be preferable. Always consult the chemical compatibility chart for specific reagents.
Q: Can a lab sink drain go directly to the sanitary sewer?
A: It depends on local regulations and the type of waste. Non-hazardous rinsate is typically allowed to go to sanitary sewers; hazardous chemical waste must follow hazardous waste procedures, may require segregation, neutralization, and specialized waste collection. Coordinate with your EH&S or local authority.
Q: Are sensor faucets suitable for labs?
A: Sensor faucets reduce contamination and conserve water but may be inappropriate where controlled flow or strong chemical exposure can damage sensors. Choose rugged sensor models rated for lab use or opt for manual or crossflow faucets with corrosion-resistant seals.
Q: How often should lab sink drains and traps be inspected?
A: Inspect traps and drain lines at least quarterly in busy labs; increase frequency where solids or precipitates are generated. Regular checks prevent clogs, leaks and sampling issues and ensure compliance with waste handling policies.
Q: What warranty and documentation should I request?
A: Request product warranty details covering materials and workmanship, chemical resistance documentation, installation manuals, and maintenance schedules. Also ask for references from similar installations and test reports where available.
If you need help selecting the right lab sink or configuring Lab Sink Cabinets for your facility, contact our sales engineering team to schedule a site review or request a quote. View product details and request support on our product page or contact us directly for personalized assistance.
Ergonomic Principles in Lab Furniture Design

Custom Lab Sink Cabinets: When to Choose Customization
Variable Air Volume Fume Hood Sash Design Buyer Guide

Maintenance Protocols That Extend Lab Countertop Lifespan
Customization
Do you offer free design consultation?
Yes, we provide our clients with free preliminary design consulting services. Our design team will provide advice based on your needs and budget, and help you develop a laboratory layout and equipment plan that meets your requirements.
What information do I need to provide to start a custom project?
In order to start a custom project, you need to provide information about the spatial layout of the laboratory, functional requirements, equipment quantity and specifications, budget, etc. If possible, you can also provide reference drawings or patterns so that we can better understand your needs.
For Products
Do you provide laboratory tables with built-in power outlets?
Yes, we offer lab tables with integrated electrical outlets, power strips, and other features to support your laboratory's equipment needs.
About Solution
Does your laboratory furniture support customization?
Yes, we provide fully customized services including size, material, color and functional design to meet customers' specific needs.
FAQS
Where are your products manufactured?
All products are manufactured in our advanced facility—the largest laboratory furniture factory in Guangzhou—ensuring strict quality control.

Lab Sink LS-08
The LS-08 Round Cup / Funnel Sink is a small-diameter, deep cup sink designed as a funnel-type drain point on laboratory worktops. Constructed from chemical-resistant black PP, it features an extended threaded outlet that connects directly to drain piping.
This design is perfect for apparatus drain lines, RO reject water, condensate and other continuous or intermittent discharges where an open, funnel-like inlet is required.

Floor Mounted Lab Bench
Our Floor Mounted Lab Bench is an essential, high-efficiency workspace for laboratories, made from high-quality steel-wood or corrosion-resistant stainless steel materials to ensure exceptional durability and stability. The unique floor-mounted design effectively reduces vibration, optimizes space usage, and provides a safe and tidy laboratory environment.
Customizable storage solutions help organize lab equipment efficiently, while the easy-to-clean surface maintains laboratory hygiene. It is widely suitable for research institutions, educational laboratories, and the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.

Fume Hood
The fume hood provides safe ventilation to protect against exposure to hazardous or toxic fumes, vapors, or airborne particulate. It is primarily used in laboratory and manufacturing applications to protect the user or environment outside the hood, but can also be used to protect the materials or experiment under the hood.
APPLICATION
Chemistry Lab, physics Lab, biological analysis, pharmaceutical medicine analysis, biological pharmaceutical, plant culture, environmental testing and electronic instrumentation scientific research and so on.

Flammable Storage Cabinet
Safety Cabinets store flammable liquids, corrosives, pesticides and other hazardous materials. All fire-resistant safety cabinets by meet fire codes and regulations for safety storage.
To help protect your people and facility from a potential fire, safety cabinets are engineered to safely contain flammable fuels, solvents, and chemicals. Safety cabinets can not only help everyone store chemicals reasonably, save chemical supplies, but also save human resources, and avoid fires caused by chemicals with the greatest strength.



 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
MaxLabFurniture
MaxLab Furniture
daihongada
Max Laboratory